Arithmetic logic unit
Appearance
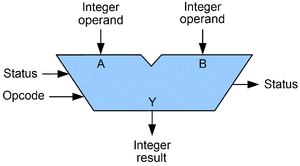
- Arithmetic logic unit
- In Logic World, an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) is a component of a central processor that performs basic arithmetic and logic operations.
- By combining multiple operations, it is possible to perform any computation.
- It may be called the "brains" of the central processor.
An ALU also has "flags" to keep track of different situations during computation. Operations that an ALU can perform include arithmetic operations such as addition and subtraction, as well as bitwise operations like XOR, NOR, AND, and OR.
The status flags it keeps track of are, for example:
- A = B
- A > B
- A < B
- Carry
- Others
ALUs can have very different designs with varying specifications, such as bit size, possible operations, and speed. In principle, you don't need to implement every possible operation - a few operations are sufficient to make the system Turing complete - although additional operations make it more convenient and often faster.
Example
Below is an example of possible operations in an ALU:
| Name | Opcode | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Add | 000 | Adds A and B |
| Sub | 001 | Subtracts B from A |
| AND | 010 | Outputs true if both A and B are true, otherwise false |
| NAND | 011 | Inverse of AND. If A and B are true, output is false |
| OR | 100 | Outputs true if either A or B is true |
| NOR | 101 | Inverse of OR. If either A or B is true, output is false |
| XOR | 110 | Outputs true if exactly one of A or B is true |
ALU Designs
Their are two main alu Designs:
- Mux Based ALU's
- Control Line based ALU's

