Multiplexer: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Lawrziepan (talk | contribs) Initial creation |
FoxFireFive (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Multiplexer Diagram.png|300x300px|A diagram of a multiplexer|alt=A diagram of a multiplexer|thumb]][[File:Multiplexer Circuit.png | [[File:Multiplexer Diagram.png|300x300px|A diagram of a multiplexer|alt=A diagram of a multiplexer|thumb]] | ||
[[File:Simpler Multiplexer Circuit.png|alt=A diagram of a simple multiplexer|thumb|376x376px|Example of a simple multiplexer.]] | |||
A multiplexer's job is to select from the input data using a select input. A multiplexer(or MUX) is an essential piece of any circuit in Logic World. There are many different ways to build a multiplexer. | |||
== | == Behavior == | ||
A multiplexer has at least 2 inputs of any bit size, and a select input that is either: | A multiplexer has at least 2 inputs of any bit size, and a select input that is either: | ||
| Line 8: | Line 10: | ||
== Uses == | == Uses == | ||
Multiplexers are very versatile, and can be used for many circuits. Multiplexers are | Multiplexers are very versatile, and can be used for many circuits. Multiplexers are commonly used for: | ||
* Selecting between registers to use in operations | * Selecting between registers to use in operations in a CPU. | ||
* Indexing memory. | * Indexing memory. | ||
Revision as of 21:18, 7 September 2025
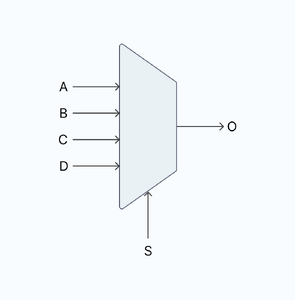
A multiplexer's job is to select from the input data using a select input. A multiplexer(or MUX) is an essential piece of any circuit in Logic World. There are many different ways to build a multiplexer.
Behavior
A multiplexer has at least 2 inputs of any bit size, and a select input that is either:
- A bit array with a length of the number of inputs, and whichever bits are ON, their corresponding inputs get bitwise-ORed to the output.
- A value which corresponds to an input to send directly to the output.
Uses
Multiplexers are very versatile, and can be used for many circuits. Multiplexers are commonly used for:
- Selecting between registers to use in operations in a CPU.
- Indexing memory.

