Arithmetic logic unit: Difference between revisions
Appearance
m Fixed grammer mystakes. |
m added the alu example. :3 |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:ALU.gif|thumb|A symbolic representation of an ALU. The arrows represent inputs and outputs.]] | [[File:ALU.gif|thumb|A symbolic representation of an ALU. The arrows represent inputs and outputs.]] | ||
[[File:Alu-8-bit.png|thumb|This is what a control line alu looks like it has inputs A and B, !A, !B, Carry, XOR, AND, OR.]] | |||
The ALU is a component in a computer that does the actal processing in a computer, it has an opcode input and inputs for A and B. Its like the brains of the computer. It can add two numbers or subtract two numbers. It can also do bitwise operations. Like XOR, NOR, AND, OR, is 0, is -, carry. It can do flags like A = B, A > B, A < B. | The ALU is a component in a computer that does the actal processing in a computer, it has an opcode input and inputs for A and B. Its like the brains of the computer. It can add two numbers or subtract two numbers. It can also do bitwise operations. Like XOR, NOR, AND, OR, is 0, is -, carry. It can do flags like A = B, A > B, A < B. | ||
Revision as of 13:46, 14 September 2025
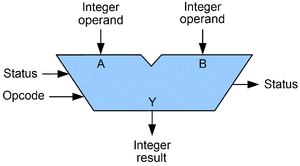
The ALU is a component in a computer that does the actal processing in a computer, it has an opcode input and inputs for A and B. Its like the brains of the computer. It can add two numbers or subtract two numbers. It can also do bitwise operations. Like XOR, NOR, AND, OR, is 0, is -, carry. It can do flags like A = B, A > B, A < B.
Example of what opcodes may look like:
| Name | Opcode | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Add | 000 | Adds A and B |
| Sub | 001 | Subtracts A and B |
| AND | 010 | if A and B are true then output true else output false |
| NAND | 011 | invert of AND if A and B is true then output false |
| OR | 100 | either A or B |
| NOR | 101 | invert of OR |
| XOR | 110 | OR of A and B but if both are true then output false |

