Fast Buffer
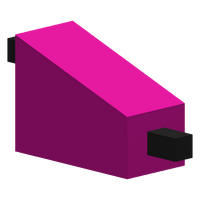 Fast Buffer | |
| Component info | |
|---|---|
| Internal ID |
MHG.Buffer |
| Configurable | No |
| Input and output | |
| Input count | 2 |
| Output count | 0 |
| Propagation delay | 0 ticks |
The Fast Buffer is a component used for digital logic. It has two inputs, with one higher up than the other. The lower input will be ON if the upper input is ON, but not vice-versa; in this way, the component "buffers" the signal by only allowing it to travel one way.
The Fast Buffer is similar to the Buffer, but:
- It takes up more space
- It uses two inputs, instead of one input and one output
- It updates in zero ticks instead of one
Buffers are commonly used to optimize circuits for speed. Their unique zero-tick logic allows time to be saved in many circuits.
Behavior
The Fast Buffer's two inputs are linked, with the lower input following the state of the upper input.
| Higher Input | Lower Input |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 |
The lower input updates it state in the same tick that the upper input changes state.
Because the lower peg is an input and not an output, if multiple circuits are attached directly to the lower peg, signals can flow between them, unlike with regular Buffers. If this behavior is undesirable for your circuit, you can add additional Fast Buffers, one for each section of the circuit you want to keep isolated.
Placement
Fast Buffers have two attachment points, one for each square covered by the body of the component. These attachment points can be placed in the center of a Circuit Board square or on top of a Mount.

